We Figured Out How AI Overviews Work (& Built A Tool To Prove It)
This post was sponsored by Market Brew. The opinions expressed in this article are the sponsor’s own.
Wondering how to realign your SEO strategy for maximum SERP visibility in AI Overviews (AIO)?
Do you wish you had techniques that mirror how AI understands relevance?
Imagine if Google handed you the blueprint for AI Overviews:
- Every signal.
- Every scoring mechanism.
- Every semantic pattern it uses to decide what content makes the cut.
That’s what our search engineers did.
They reverse-engineered how Google’s AI Overviews work and built a model that shows you exactly what to fix.
It’s no longer about superficial tweaks; it’s about aligning with how AI truly evaluates meaning and relevance.
In this article, we’ll show you how to rank in AIO SERPs by creating embeddings for your content and how to realign your content for maximum visibility by using AIO tools built by search engineers.
The 3 Key Features Of AI Overviews That Can Make Or Break Your Rankings
Let’s start with the basic building blocks of a Google AI Overviews (AIO) response:
What Are Embeddings?
Embeddings are high-dimensional numerical representations of text. They allow AI systems to understand the meaning of words, phrases, or even entire pages, beyond just the words themselves.
Rather than matching exact terms, embeddings turn language into vectors, or arrays of numbers, that capture the semantic relationships between concepts.
For example, “car,” “vehicle,” and “automobile” are different words, but their embeddings will be close in vector space because they mean similar things.
Large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT or Google Gemini use embeddings to “understand” language; they don’t just see words, they see patterns of meaning.
Why Do Embeddings Matter For SEO?
Understanding how Large Language Models (LLMs) interpret content is key to winning in AI-driven search results, especially with Google’s AI Overviews.
Search engines have shifted from simple keyword matching to deeper semantic understanding. Now, they rank content based on contextual relevance, topic clusters, and semantic similarity to user intent, not just isolated words.
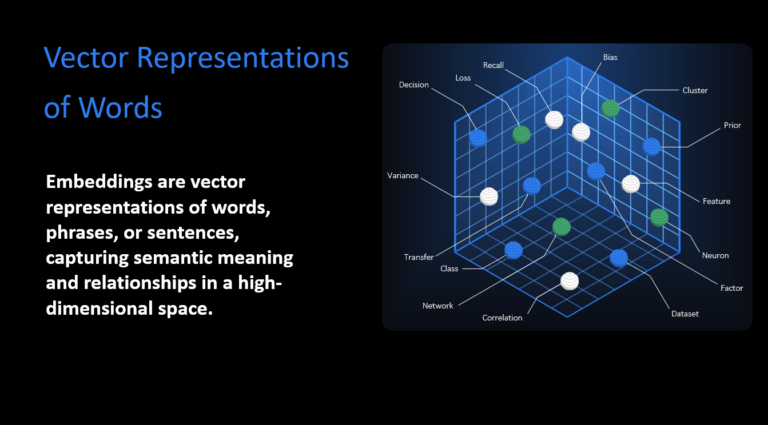 Image created by MarketBrew.ai, April 2025
Image created by MarketBrew.ai, April 2025Embeddings power this evolution.
They enable search engines to group, compare, and rank content with a level of precision that traditional methods (like TF-IDF, keyword density, or Entity SEO) can’t match.
By learning how embeddings work, SEOs gain tools to align their content with how search engines actually think, opening the door to better rankings in semantic search.
 Image created by MarketBrew.ai, April 2025
Image created by MarketBrew.ai, April 2025How To Rank In AIO SERPs By Creating Embeddings
Step 1: Set Up Your OpenAI Account
- Sign Up or Log In: If you haven’t already, sign up for an account on OpenAI’s platform at https://platform.openai.com/signup.
- API Key: Once logged in, you’ll need to generate an API key to access OpenAI’s services. You can find this in your account settings under the API section.
Step 2: Install The OpenAI Python Client To Simplify This Step For SEO Pros
OpenAI provides a Python client that simplifies the process of interacting with their API. To install it, run the following command in your terminal or command prompt:
pip install openaiStep 3: Authenticate With Your API Key
Before making requests, you need to authenticate using your API key. Here’s how you can set it up in your Python script:
import openai
openai.api_key = 'your-api-key-here'Step 4: Choose Your Embedding Model
At the time of this article’s creation, OpenAI’s text-embedding-3-small is considered one of the most advanced embedding models. It is highly efficient for a wide range of text processing tasks.
Step 5: Create Embeddings For Your Content
To generate embeddings for text:
response = openai.Embedding.create(
model="text-embedding-3-small",
input="This is an example sentence."
)
embeddings = response['data'][0]['embedding']
print(embeddings)The result is a list of numbers representing the semantic meaning of your input in high-dimensional space.
Step 6: Storing Embeddings
Store embeddings in a database for future use; tools like Pinecone or PostgreSQL with pgvector are great options.
Step 7: Handling Large Text Inputs
For large content, break it down into paragraphs or sections and generate embeddings for each chunk.
Use similarly sized chunks for better cosine similarity calculations. To represent an entire document, you can average the embeddings for each chunk.
💡Pro Tip: Use Market Brew’s free AI Overviews Visualizer. The search engineer team at Market Brew has created this visualizer to help you understand exactly how embeddings, the fourth generation of text classifiers, are used by search engines.
Semantics: Comparing Embeddings With Cosine Similarity
Cosine similarity measures the similarity between two vectors (embeddings), regardless of their magnitude.
This is essential for comparing the semantic similarity between two pieces of text.
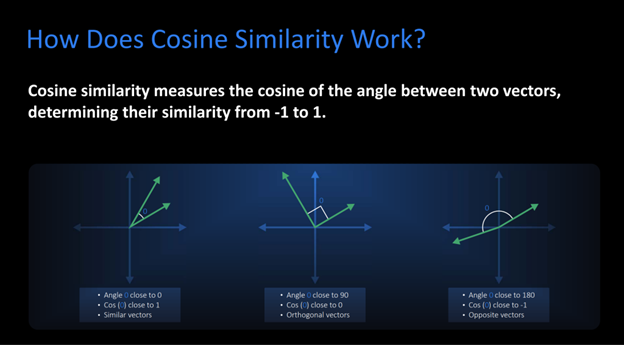 Image created by MarketBrew.ai, April 2025
Image created by MarketBrew.ai, April 2025Typical search engine comparisons include:
- Keywords with paragraphs,
- Groups of paragraphs with other paragraphs, and
- Groups of keywords with groups of paragraphs.
Next, search engines cluster these embeddings.
How Search Engines Cluster Embeddings
Search engines can organize content based on clusters of embeddings.
In the video below, we are going to illustrate why and how you can use embedding clusters, using Market Brew’s free AI Overviews Visualizer, to fix content alignment issues that may be preventing you from appearing in Google’s AI Overviews or even their regular search results!
Embedding clusters, or “semantic clouds”, form one of the most powerful ranking tools for search engineers today.
Semantic clouds are topic clusters in thousands of dimensions. The illustration above shows a 3D representation to simplify understanding.
Topic clusters are to entities as semantic clouds are to embeddings. Think of a semantic cloud as a topic cluster on steroids.
Search engineers use this like they do topic clusters.
When your content falls outside the top semantic cloud – what the AI deems most relevant – it is ignored, demoted, or excluded from AI Overviews (and even regular search results) entirely.
No matter how well-written or optimized your page might be in the traditional sense, it won’t surface if it doesn’t align with the right semantic cluster that the finely tuned AI system is seeking.
By using the AI Overviews Visualizer, you can finally see whether your content aligns with the dominant semantic cloud for a given query. If it doesn’t, the tool provides a realignment strategy to help you bridge that gap.
In a world where AI decides what gets shown, this level of visibility isn’t just helpful. It’s essential.
Free AI Overviews Visualizer: How To Fix Content Alignment
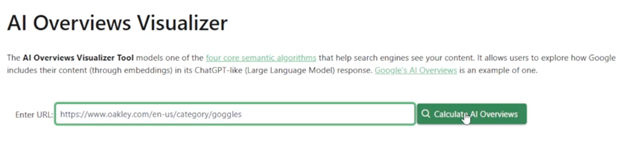
Step 1: Use The Visualizer
Input your URL into this AI Overviews Visualizer tool to see how search engines view your content using embeddings. The Cluster Analysis tab will display embedding clusters for your page and indicate whether your content aligns with the correct cluster.
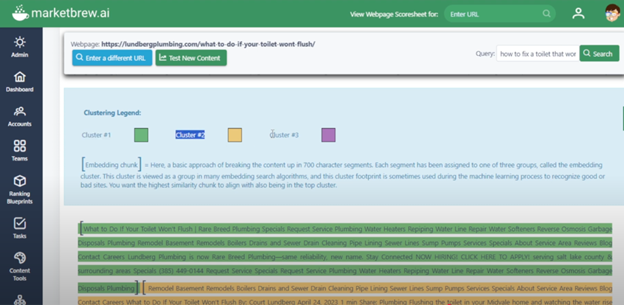 Screenshot from MarketBrew.ai, April 2025
Screenshot from MarketBrew.ai, April 2025Step 2: Read The Realignment Strategy
The tool provides a realignment strategy if needed. This provides a clear roadmap for adjusting your content to better align with the AI’s interpretation of relevance.
Example: If your page is semantically distant from the top embedding cluster, the realignment strategy will suggest changes, such as reworking your content or shifting focus.
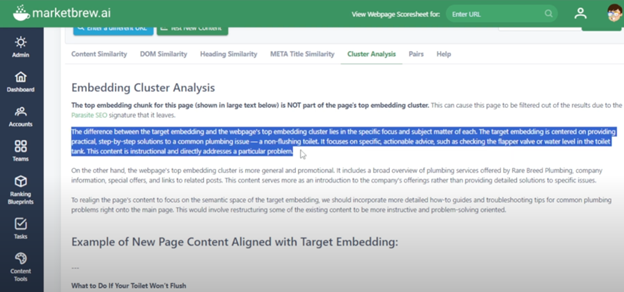 Screenshot from MarketBrew.ai, April 2025
Screenshot from MarketBrew.ai, April 2025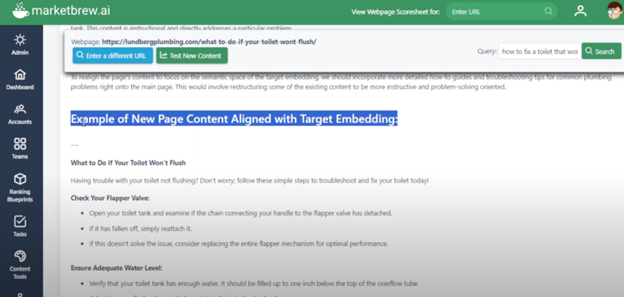 Screenshot from MarketBrew.ai, April 2025
Screenshot from MarketBrew.ai, April 2025Step 3: Test New Changes
Use the “Test New Content” feature to check how well your content now fits the AIO’s top embedding cluster. Iterative testing and refinement are recommended as AI Overviews evolve.
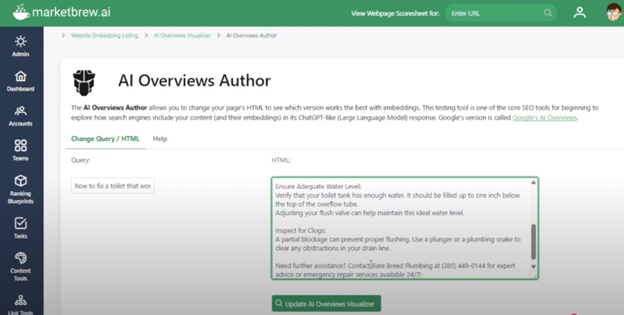 Screenshot by MarketBrew.ai, April 2025
Screenshot by MarketBrew.ai, April 2025See Your Content Like A Search Engine & Tune It Like A Pro
You’ve just seen under the hood of modern SEO – embeddings, clusters, and AI Overviews. These aren’t abstract theories. They’re the same core systems that Google uses to determine what ranks.
Think of it like getting access to the Porsche service manual, not just the owner’s guide. Suddenly, you can stop guessing which tweaks matter and start making adjustments that actually move the needle.
At Market Brew, we’ve spent over two decades modeling these algorithms. Tools like the free AI Overviews Visualizer give you that mechanic’s-eye view of how search engines interpret your content.
And for teams that want to go further, a paid license unlocks Ranking Blueprints to help track and prioritize which AIO-based metrics most affect your rankings – like cosine similarity and top embedding clusters.
You have the manual now. The next move is yours.
Image Credits
Featured Image: Image by Market Brew. Used with permission.
In-Post Image: Images by Market Brew. Used with permission.